Redness and Rosacea
Redness to the skin is a very common treatment indication that we see at Youth Lab and one that is experienced by many people at some time in their life. The condition can cause psychological and self-confidence issues, which in turn, can affect social and professional interactions.
A common skin condition causing redness, flushing and visible capillaries is known a Rosacea. It is an inflammatory skin disease affecting the face and the underlying cause is yet to be determined. There is a strong genetic link and association with skin bacteria and mites (demodex mite).
Rosacea can also be triggered by diet (gluten and pro-inflammatory foods), alcohol, hot/spicy foods, emotional stress, smoking and heat. There is no known cure but the symptoms can be managed effectively with regular treatments and an understanding of the underlying triggers.
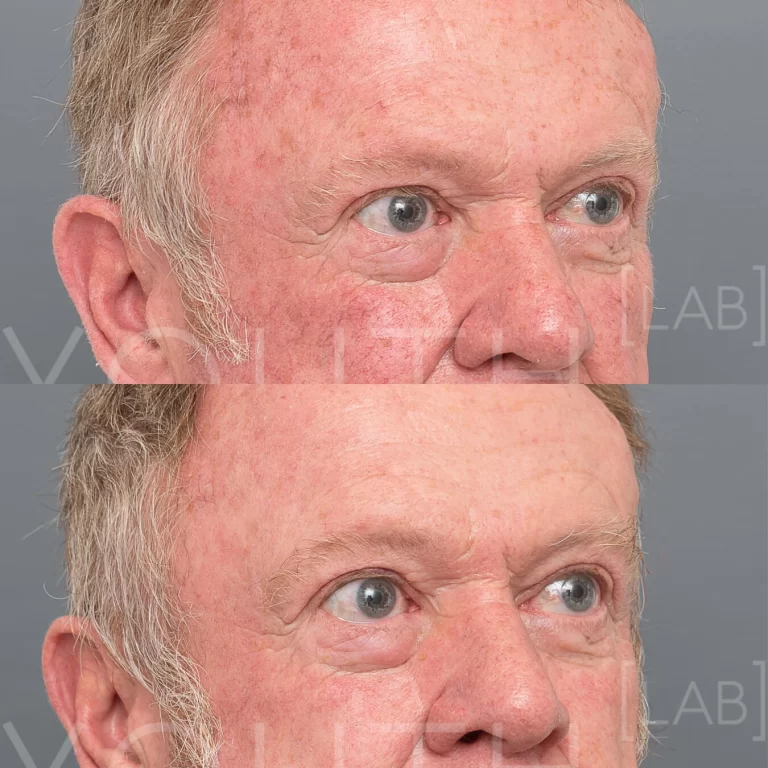
Rosacea is a combination of a damaged capillary network, redness and inflammatory lesions occurring on the cheeks, nose and forehead. Often the small surface capillaries of the face enlarge and give the appearance of permanent flushing. The inflammatory lesions or pustules can often be misdiagnosed as acne. Not every person presents the same and rosacea is often misdiagnosed for many years.
Rosacea often occurs between the ages of 30 and 50 with frequent flushing or blushing being the first sign. The symptoms tend to worsen with advancing age. Both men and women can be affected by the condition.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of Rosacea?
Rosacea can be classified into 3 stages.
Stage 1
Persistent erythema (redness) and visible capillaries
Stage 2
Stage 1 accompanied with papules and pustules
Stage 3
Stage 1 and 2 accompanied with significant swelling. In men, severe rosacea can cause the nose to become reddened and enlarged (rhinophyma)
The Symptoms of rosacea include:
- Telangiectasia and enlarged capillaries
- Flushing and blushing of the cheeks
- Pustules and pimple like lesions (often mistaken for acne)
- Lumps under the skin
- Swelling of the cheeks and nose leading to rhinophyma
- Burning and stinging sensations
What are the causes of Rosacea?
The underlying cause of Rosacea is unknown, though it is thought to be genetically linked, and demodex mite is suspected to be involved in the majority of cases.
There are also triggers for the condition which include:
- Alcohol
- Gluten
- Hot/spicy foods
- Smoking
- Caffeine
- Hot drinks
- Sunlight
- Anxiety
- Emotional stress
- Overheating, especially in bed at night
- Hot showers
- Extremes of temperature
What are the treatments for Rosacea?
Treatments are generally continuous in order to give an ongoing reduction of Rocasea.
The most important treatment of Rosacea is complete avoidance of known triggers. It is especially important to avoid overheating, hot showers and prolonged exposure to sunlight. An elimination diet of all known dietary triggers to decrease inflammation is also recommended.
In more severe cases, antibiotics such as Doxycycline and Minocycline may be used to help treat the inflammation and are thought to act against the mites/bacteria that are implicated in the condition.
These will start to work in 4-6 weeks and need to be continued until the resolution of symptoms (often a 3 month course is needed but occasional long term use may be required). Topical antibiotics and antiparasitic agents such as Metronidazole and Ivermectin may also be applied to the skin.
The use of appropriate home skin care is essential. With products to prevent redness and flushing, support the skin’s protective barrier and decrease inflammation within the skin.
This may mean ceasing all current products (such as over the counter cosmetics) and establishing a new skin care routine with basic products. Daily broad spectrum SPF is also essential.
Other treatment options depend on the severity of the condition. The goals of treatment are to reduce the appearance of the superficial blood vessels and redness, decrease cellular damage, encourage healthy new blood vessel formation and treat inflammation.
What are our recommended treatments?
It is important to remember that there is no cure to rosacea, however the symptoms can be managed and controlled long term with regular treatments and avoidance of triggers.
As with many of the treatment recommendations at Youth Lab, a combination of treatments may be required for optimal results.
Please note that the below is a reference point and full treatment recommendations will be made following a consultation.
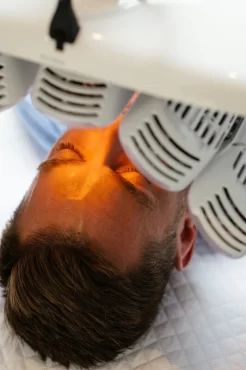
Healite II LED
The Healite II LED utilises low level light therapy to treat the skin superficially by delivering pure light to the skin which in turn utilises your body’s own cellular recovery. This in turn treats the inflammation associated with Rosacea as well as improving the appearance of redness.
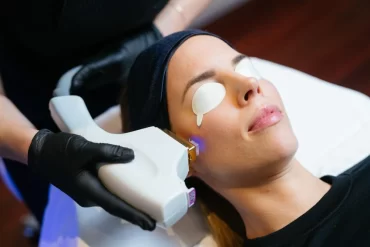
BBL Corrective
Broadband light is used to treat the superficial capillaries, decrease cellular damage, encourage healthy new blood vessel formation and treat inflammation.
Medical Peels
Certain medical peels such as Mandelic acid work to prevent redness and flushing, support the skin’s protective barrier and decrease inflammation within the skin.
Halo Laser
Halo laser is used to decrease the redness and treat the damaged capillaries, laser can also be used to remove disfiguring rhinophyma.
Skin Needling
Skin needling can be used to stimulate a wound healing response in the skin and encourage cell renewal. Using anti-redness serums and hydrating serums these can be infused into the skin to help with the symptoms of redness and dehydration.