Redness and Rosacea
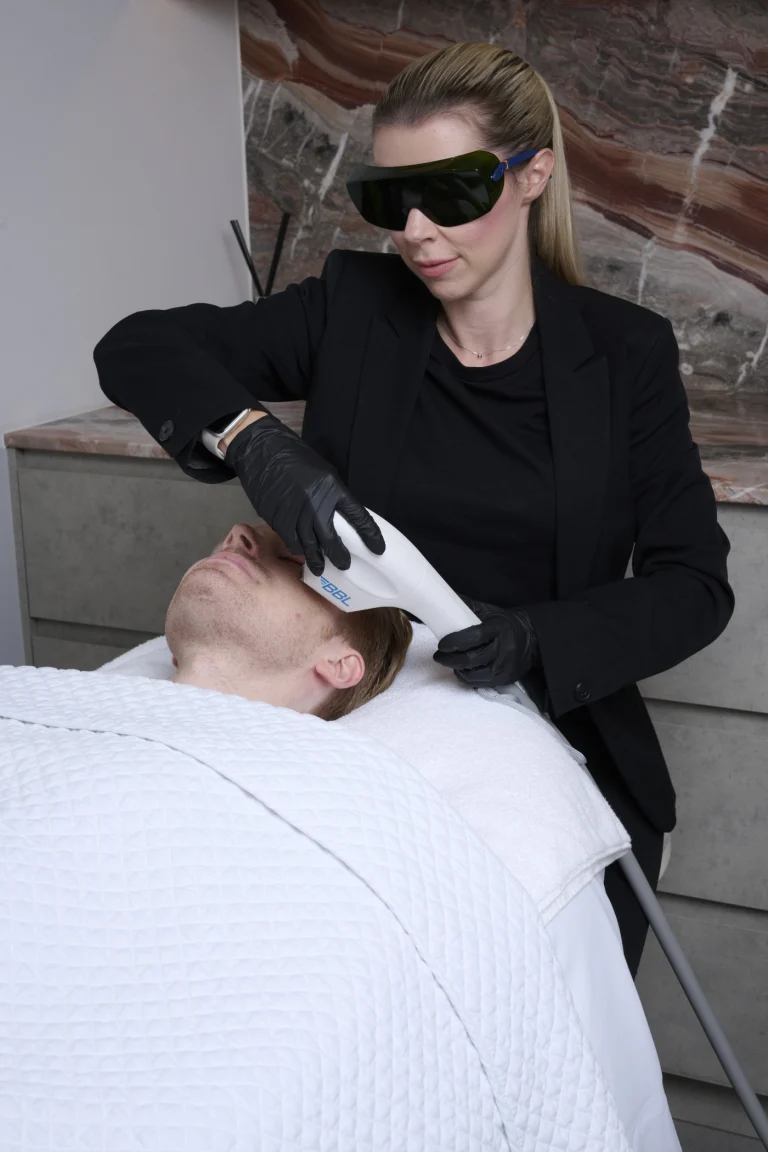

Some individuals experience redness, flushing or visible capillaries, which may relate to rosacea or other conditions.
Rosacea is one of the most common skin concerns we see at Youth Lab. For some people, it can appear as persistent flushing or visible capillaries, while for others it comes and goes, often linked to environmental or lifestyle triggers. Regardless of severity, many clients find that ongoing rosacea affects their self-confidence and comfort in social or professional settings.
In accordance with Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulations, we are unable to provide detailed information about specific treatments online. Such information may be misinterpreted as the promotion of prescription-only (Schedule 4) medications – this is not permitted under TGA guidelines.
For this reason, a consultation with one of our practitioners is required. During your comprehensive consultation, your practitioner will carefully assess your skin, discuss your concerns, and provide education around suitable treatment options. A personalised treatment plan will then be created to address your individual needs.
Treatment costs will vary depending on your tailored plan and will be discussed with you in detail during your consultation.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of Rosacea?
Telangiectasia and enlarged capillaries
Flushing and blushing of the cheeks
Pustules and pimple like lesions (often mistaken for acne)
Lumps under the skin
Swelling of the cheeks and nose leading to rhinophyma
Burning and stinging sensations
Rosacea can be classified into 3 stages.
Stage 1
Persistent erythema (redness) and visible capillaries
Stage 2
Stage 1 accompanied with papules and pustules
Stage 3
Stage 1 and 2 accompanied with significant swelling. In men, severe rosacea can cause the nose to become reddened and enlarged (rhinophyma)
What contributed to Rosacea?
A number of internal and external factors can contribute, including:
Genetics and family history
Environmental stressors such as UV exposure or extreme temperatures
Certain foods or drinks (e.g. hot/spicy meals, alcohol, caffeine)
Emotional stress or anxiety
Lifestyle factors such as smoking
Skin sensitivity to products or changes in the skin barrier
While ROSACEA can affect anyone, it is most commonly seen in adults between the ages of 30–50, and often becomes more noticeable over time.
Can Rosacea be prevented?
Avoiding triggers is key.
This may include:
Daily use of a broad spectrum SPF 50+
Avoiding excessive sun exposure and hot environments
Limiting alcohol, caffeine, or spicy foods if they worsen flushing
Using gentle, fragrance-free skincare to maintain barrier function
Managing stress and supporting general wellbeing
What are our recommended treatments?
At Youth Lab, we provide a range of evidence-based treatments that may help improve the cosmetic appearance of rosacea and visible capillaries. A consultation with one of our practitioners is essential to determine the best approach for your skin.
Options may include:
Healite II LED – low-level light therapy to calm and support the skin.
BBL Corrective – broadband light energy that can reduce the visible appearance of rosacea and capillaries in suitable candidates.
ClearV Vascular Laser – ClearV Vascular Laser is a targeted light-based treatment designed to improve the visible appearance of benign vascular concerns such as superficial veins, capillaries, and angiomas on the face and body,
Gentle peels – such as mandelic acid, designed to strengthen the skin barrier and support hydration.
Halo laser resurfacing – for selected clients, to improve overall skin quality and reduce signs of rosacea and sun damage.
Skin needling with serums – to support healthy skin renewal and hydration, which may help with diffuse rosacea.
Your practitioner will tailor a plan based on your individual concerns, triggers, and skin type.
Please note:
Rosacea can be ongoing, and there is no “cure.”
The goal of treatment is to manage symptoms, strengthen the skin, and improve appearance over time.
Results vary depending on skin type, lifestyle, and commitment to ongoing care.
In some cases, referral to a GP or dermatologist may be recommended to explore underlying causes.